On its own, Darktrace/Email™ stops attacks before they reach an employee’s inbox and considers both security teams and the employees themselves. But its value extends beyond email security, increased by its ability to integrate with the wider security ecosystem, including both Darktrace products and external tools.
Darktrace’s understanding of you and your organization can be applied anywhere your company has data. This unifying approach to cyber security feeds AI outputs into each other, from threat prevention to detection and response, in order to harden the entire security posture autonomously and continuously. The AI also enriches other security solutions an organization has in place by both ingesting and sharing data. This degree of integration transforms a security stack so that it is greater than the sum of its parts.
Integrating Beyond Email to Enhance Detection and Response
Integrating email security with other areas of the digital estate bolsters defenses, while reducing required resources. With more data, security teams gain a better understanding of the security stack and how attacks move through the system.
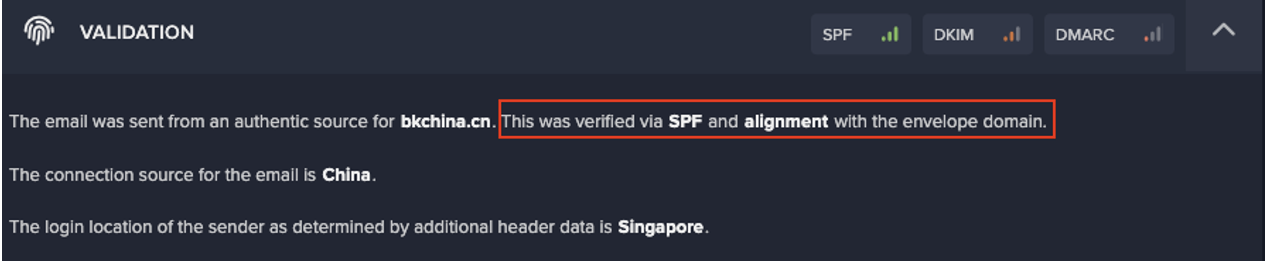
Traditional security solutions do this by either manually aggregating inputs from various tools or using a SIEM without native integrations to collate data. In contrast, Darktrace’s integration provides real-time intelligence communications between products to inform security teams.
For example, context of network activity can provide more holistic email security. There’s a strong correlation between the websites users visit and the people that they email, which means information like web traffic provides insight into email threats, and vice versa.
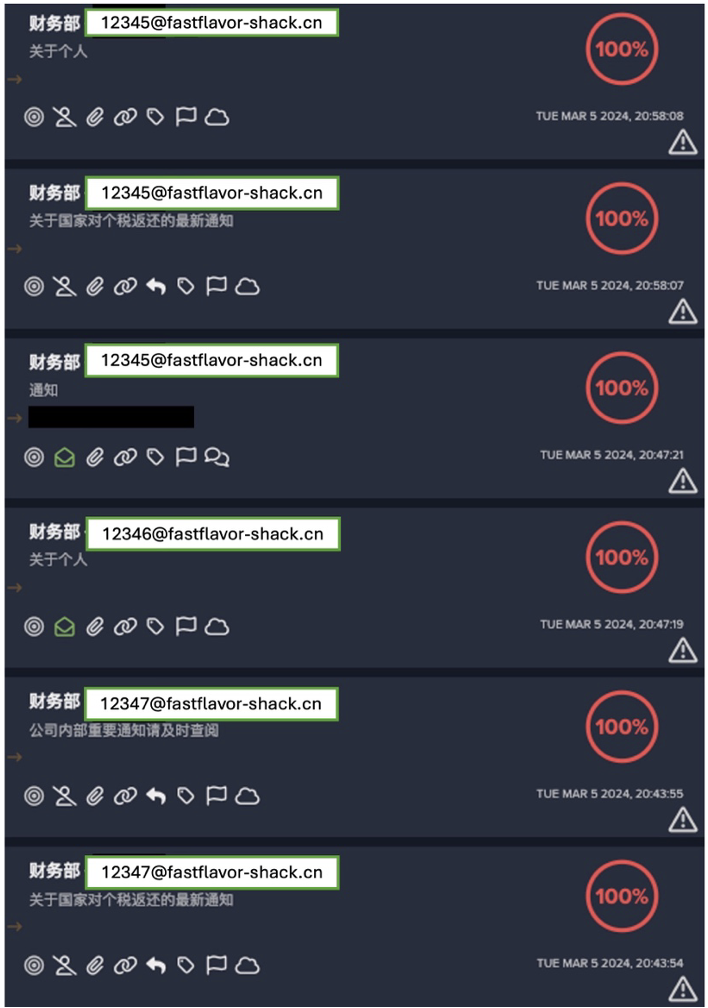
If an organization receives an email from a strange new sender, that happens to be have been sent from a domain nobody has ever visited, that added context could influence the aggression levels of actions taken. Integrations with endpoint security extends this type of informed decision-making to remote environments. These examples highlight the patented power of Darktrace/Network™ and Darktrace/Endpoint™ when paired with email coverage.

Email activity is tied to cloud/SaaS application account activity in an even more direct way. In the case of an account takeover, a suspicious Microsoft 365 login becomes even more suspicious if it is followed by highly unusual email activity, like new inbox rules being created. Too many email security solutions focus on the inbox alone, but viewing these areas in a single scope is critical for security teams wanting to understand the full timeline of an incident.
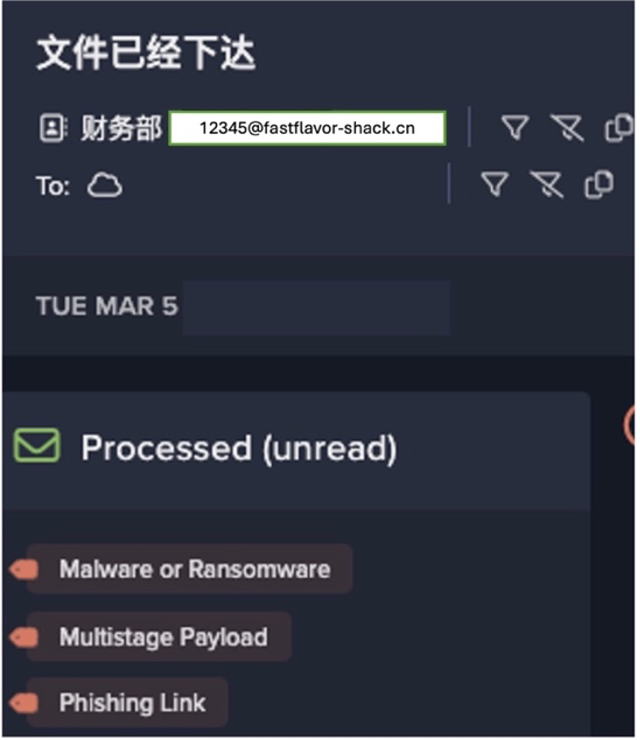
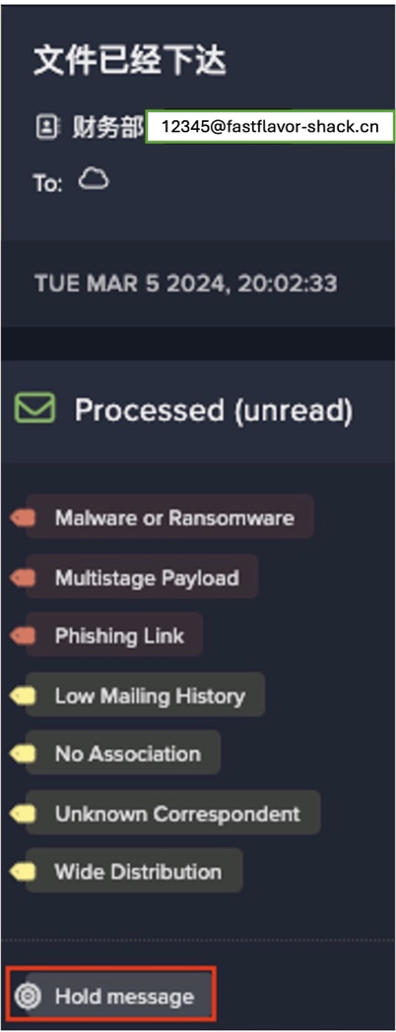
To this end, Darktrace creates a 360-degree view of each user and their behavior. This comprehensive view goes beyond native security monitoring tools, allowing security teams to identify instances of data exfiltration, human error, misdirected emails, inappropriate link sharing, unusual log activity, and more.
In one real-life example, the security team saw an attack from both an email and a SaaS perspective to quickly understand the whole picture, thanks to Darktrace/Email and Darktrace/Apps™.
Darktrace customers are getting significant value from this integrated security stack. “The whole suite of products has given us 100% visibility across our whole ecosystem, which is fantastic. A lot of times we need to use many products to do that, and with the Darktrace products, I have that all in one,” commented a vice president of enterprise security and fraud management at a major credit union.
Siloed solutions are a massive pain point in the cyber industry. Most companies have several, layered tools in their security stacks. When there is little to no communication between them, the security team must contend with an inflated workload and misses out on value. They must learn how to navigate several different dashboards, translate between languages and terms, and manually correlate data, in addition to monitoring all the solutions daily. This process makes maintaining security more difficult for the team, especially in a threat landscape with increasingly complex and fast-paced attacks.
By sending and collecting information to and from other tools that the security team already uses, whether they are a part of Darktrace’s product stack or not, Darktrace/Email optimizes workflows so security teams can reallocate resources to larger, more strategic projects.
Collaborating Across Email Security and Cyber Risk Management Tools
Syncing email protections with cyber risk management tools even further reduces risk and hardens security.
When emails are received from domain names associated with the brand of the client, an attack surface management tool can automatically analyze if those domains should be included as part of the attack surface scope or trigger malicious domain responses.
In the other direction, when the attack surface management tool identifies malicious assets, like suspicious domains, spoofing sites, and typo squatters, it can inform email security decisions. With integrations between tools, these malicious assets automatically become watched domains with heightened sensitivity for inbound email.
This integrated risk reduction can occur internally as well. When security teams look at cyber risk from an internal perspective, they may identify attack paths and high value targets within the company’s digital estate. By leveraging this understanding, Darktrace can determine which employees are critical components of potential attack paths. Once determined, the AI can test them by creating phishing simulations using details like real-life communication patterns and calendar data. These tests generate insights that feed back into Darktrace/Email to harden the environment, for example by heightening sensitivity.
This demonstrates the benefits of combining Darktrace/Email and Darktrace PREVENT™. As part of the Cyber AI Loop, these connections between email security and cyber risk management are made easy for the security team to understand and act on. One customer noted how this integration had improved its security team’s workflow.
“The more you use of Darktrace, the better it can correlate on your behalf,” said a Chief Information Officer at a construction company. “That’s why we’re all in with Darktrace now. We now have a holistic Darktrace footprint, which benefits us because we have more of the modules working on our behalf and not having to do the correlations separately or in isolation.”
Supporting Compatibility with External Security Solutions
Darktrace/Email also works together with external tools. In addition to its mature integration with email providers like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspaces, Darktrace/Email has an open architecture that makes it immensely flexible. It is both API-driven and compatible with syslog, so it can integrate with any security tool and feed into any SIEM or SOAR.
This unlimited capacity for integration allows Darktrace to detect and respond to threats more precisely with access to more data, as well as reduce the security team’s time-to-meaning by putting all relevant information in a single pane of glass.
Darktrace/Email is also part of the Darktrace Mobile App, so security teams can view notifications, reports, and remediation actions at any time, even on the go. In this way, Darktrace not only fits into the greater security posture, but also with employees’ day-to-day workflow.
Finally, Darktrace/Email supports data exports. These translate and share the data it collects within the email environment, allowing the security team to communicate key takeaways generated by Darktrace/Email to anyone within the organization. It can export directly to Microsoft Excel, or any other data analytics tool. This is especially useful for security teams as they work with other departments like IT, compliance, finance, and more.
Integrations Add Value to the Darktrace Partnership
While Darktrace/Email is a powerful tool on its own, a major source of its value comes from its compatibility with the rest of Darktrace, other tools, people, and processes.
Deploying multiple Darktrace products builds a robust security ecosystem that enhances detection while breaking down silos and improving workflows, therefore enabling the security team to take on higher-level and more strategic work. By integrating with external tools, Darktrace not only increases its own value but also maximizes the return on investment of other security solutions a team already has.