It is by now common knowledge that the vast majority of cyber-threats start with an email. In the current working conditions, this is more true than ever – with a recent study reporting a 30,000% increase in phishing, websites, and malware targeting remote users.
Many email security tools struggle to detect threats they encounter for the first time. Attackers know this and are leveraging many techniques to take advantage of this fundamental flaw. This includes automation to mutate common threat variants, resulting in a massive increase in unknown threats. Another technique, which will be the focus of this blog post, is the rapid and widespread creation of new domains in order to evade reputation checks and signature-based detection.
The recent surge in domain creation
While traditional tools have to rely on identifying campaigns and patterns across multiple emails to establish whether or not an email is malicious, Cyber AI technology doesn’t require classifying emails into buckets in order to know they don’t belong. There is no need, therefore, to actively track campaigns. But as security researchers, it’s hard to miss some trends.
Since the coronavirus outbreak, we have seen the number of domains registered related to COVID-19 increase by 130,000. In this time, 60% of all spear phishing threats neutralized by Antigena Email were related to COVID-19 or remote work. Another recent study determined that 10,000 coronavirus-related domains are created every day, with roughly nine out of ten of these either malicious or attempting to generate sales of fake products.
With attackers also taking advantage of changing online behaviors arising from the pandemic, another trend we’ve seen is the proliferation of the keyword ‘Zoom’ in some of the unpopular domains that bypassed traditional tools, as attackers leverage the video conferencing platform’s recent rise in usage.
“I believe that hackers identified coronavirus as something users are desperate to find information on. Panic leads to irrational thinking and people forget the basics of cyber security.”
— COO, Atlas VPN
I recently wrote a blog post on the idea of ‘fearware’ and why it’s so successful. Right now, people are desperate for information, and attackers know this. Cyber-criminals play into fear, uncertainty, and doubt (FUD) through a number of mechanisms, and we have since seen a variety of imaginative attempts to engage recipients. These emails range from fake ‘virus trackers’, to sending emails purporting to be from Amazon, claiming an unmanageable rise in newly registered accounts, and demanding “re-registration” of the recipient’s credit card details should they wish to keep their account.
Domain name purchasing: A vicious cycle
Purchasing thousands of new domains and sending malicious emails en masse is a tried and tested technique that cyber-criminals have been leveraging for decades. Now with automation, they’re doing it faster than ever before.
Here’s why it works.
Traditional security tools work by analyzing emails in isolation, measuring them against static blacklists of ‘known bads’. By way of analogy, the gateway tool here is acting like a security guard standing at the perimeter of an organization’s physical premises, asking every individual who enters: “are you malicious?”
The binary answer to this sole question is extracted by looking at some metadata around the email, including the sender’s IP, their email address domain, and any embedded links or attachments. They analyze this data in a vacuum, and at face value, with no consideration towards the relationship between that data, the recipient, and the rest of the business. They run reputation checks, asking “have I seen this IP or domain before?” Crucially, if the answer is no, they let them straight through.
To spell that out, if the domain is brand new, it won’t have a reputation, and as these traditional tools have a limited ability to identify potential harmful elements via any other means, they have no choice but to let them in by default.
These methods barely scratch the surface of a much wider range of characteristics that a malicious email might contain. And as email threats get ever more sophisticated, the ‘innocent until proven guilty approach’ is not enough. For a comprehensive check, we would want to ask: does the domain have any previous relationship with the recipient? The organization as a whole? Does it look suspiciously visually similar to other domains? Is this the first time we’ve seen an inbound email from this user? Has anybody in the organization ever shared a link with this domain? Has any user ever visited this link?
Legacy tools are blatantly asking the wrong questions, to which attackers know the answers. And usually, they can skirt by these inattentive security guards by paying just a few pennies for new domains.
How to buy your way in
Let’s look at the situation from an attacker’s perspective. They just need one email to land and it could be keys to the kingdom, so an upfront purchase of a few thousand new domains will almost inevitably pay off. And they’d pay the price as long as it’s working and they’re profiting.
This is exactly what attackers are doing. Newly-registered domains consistently get through gateways until these traditional tools are armed with enough information to determine that the domains are bad, by which point thousands or even millions of emails could have been successfully delivered. As soon as the attack infrastructure is worn out, the attackers will abandon it, and very easily just purchase and deploy a new set of domains.
And so, the vicious cycle continues. Like a game of ‘whack-a-mole’, these legacy ‘solutions’ will continue to hammer down on recognized ‘bad’ emails – all the while more malicious domains are being created in the thousands in preparation for the next campaign. This is the ‘Domain Game’, and it’s a hard game for defenders to win.
Asking the right questions
Thankfully, the solution to this problem is as simple as the problem itself. It requires a movement away from the legacy approach and towards deploying technology that is up to par with the speed and scale of today’s attackers.
In the last two years, new technologies have emerged that leverage AI, seeking to understand the human behind the email address. Rather than inspecting incoming traffic at the surface-level and asking binary questions, this paradigm shift away from this insufficient legacy approach asks the right questions: not simply “are you malicious?”, but crucially: “do you belong?”
Informed by a nuanced understanding of the recipient, their peers, and the organization at large, every inbound, outbound, and internal email is analyzed in context, and is then re-analyzed over and over again in light of evolving evidence. Asking the right questions and understanding the human invariably sets a far higher standard for acceptable catch rates with unknown threats on first encounter. This approach far outpaces traditional email defenses which have proven to fail and leave companies and their employees vulnerable to malicious emails sitting in their inboxes.
Rather than desperately bashing away at blacklisted domains and IP addresses in an ill-fated attempt to beat the attackers, we can change the game altogether, tilting the scales in favor of the defenders – securing our inboxes and our organizations at large.
Learn more about Antigena Email


































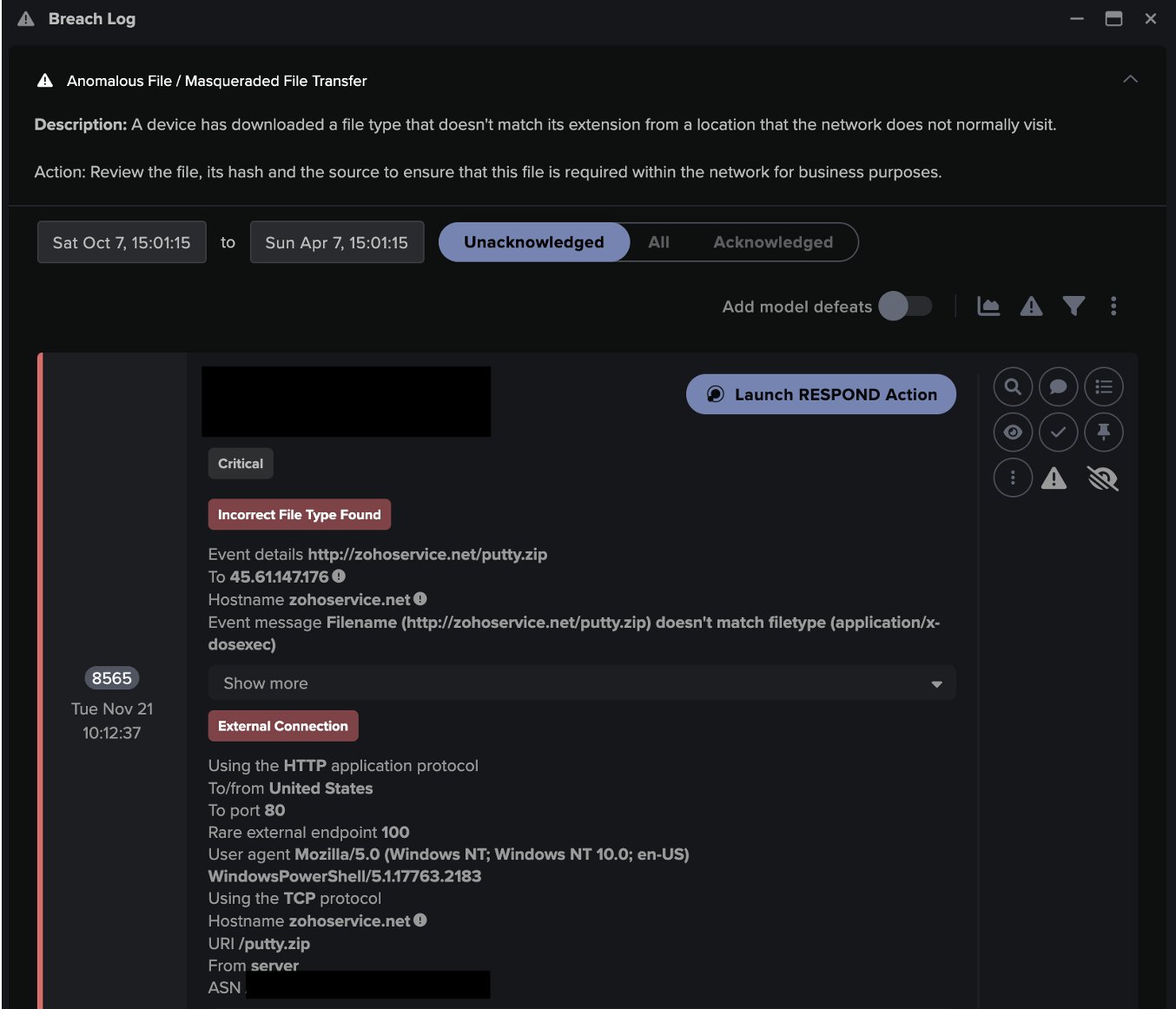
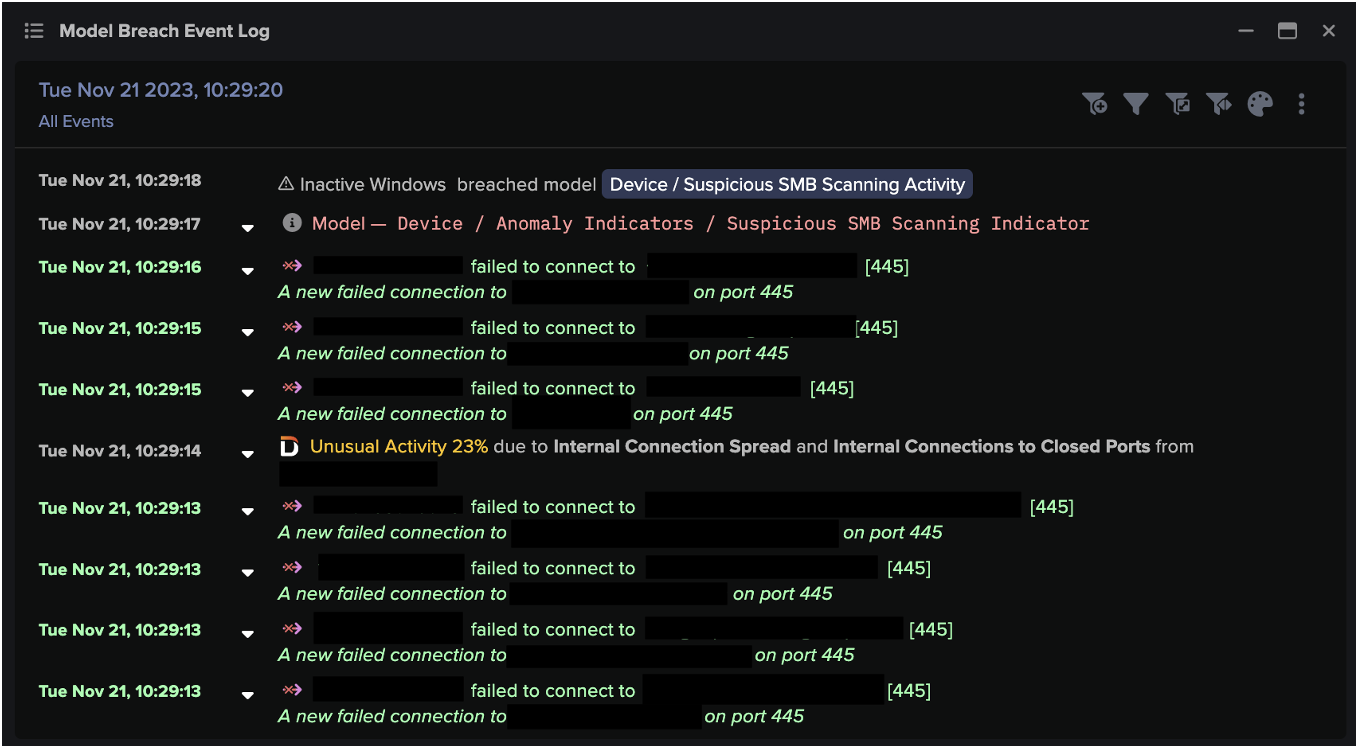
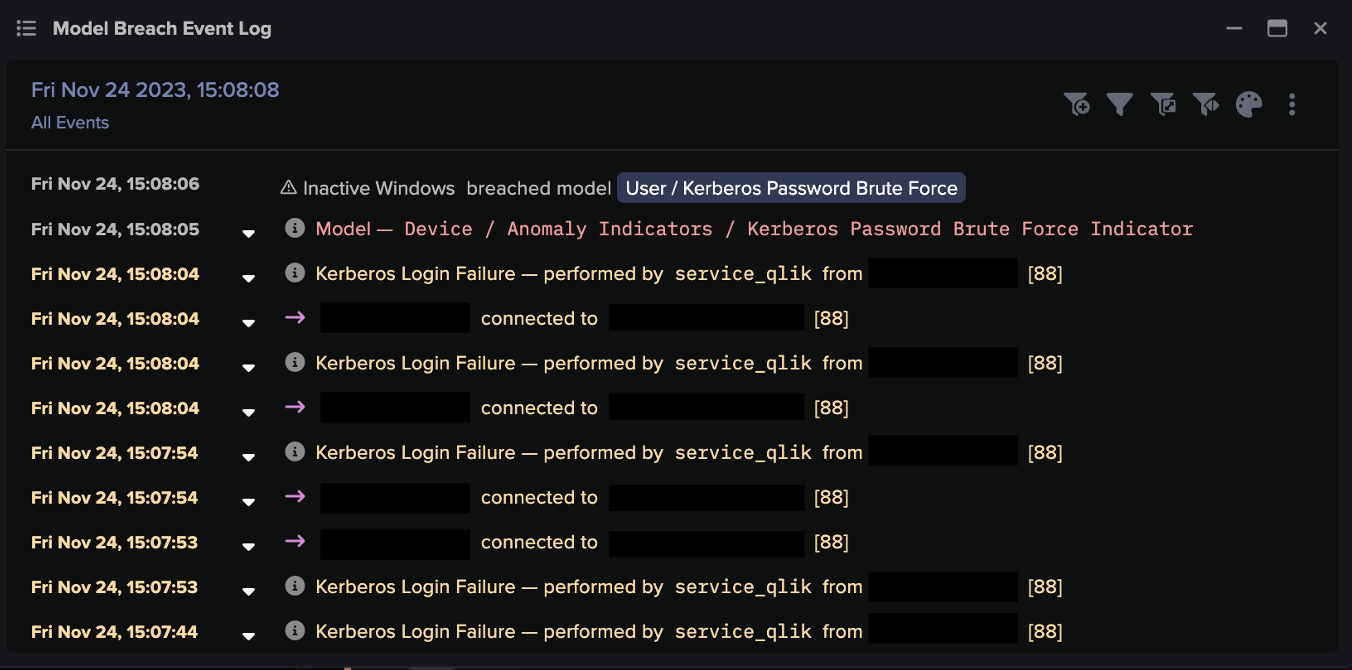
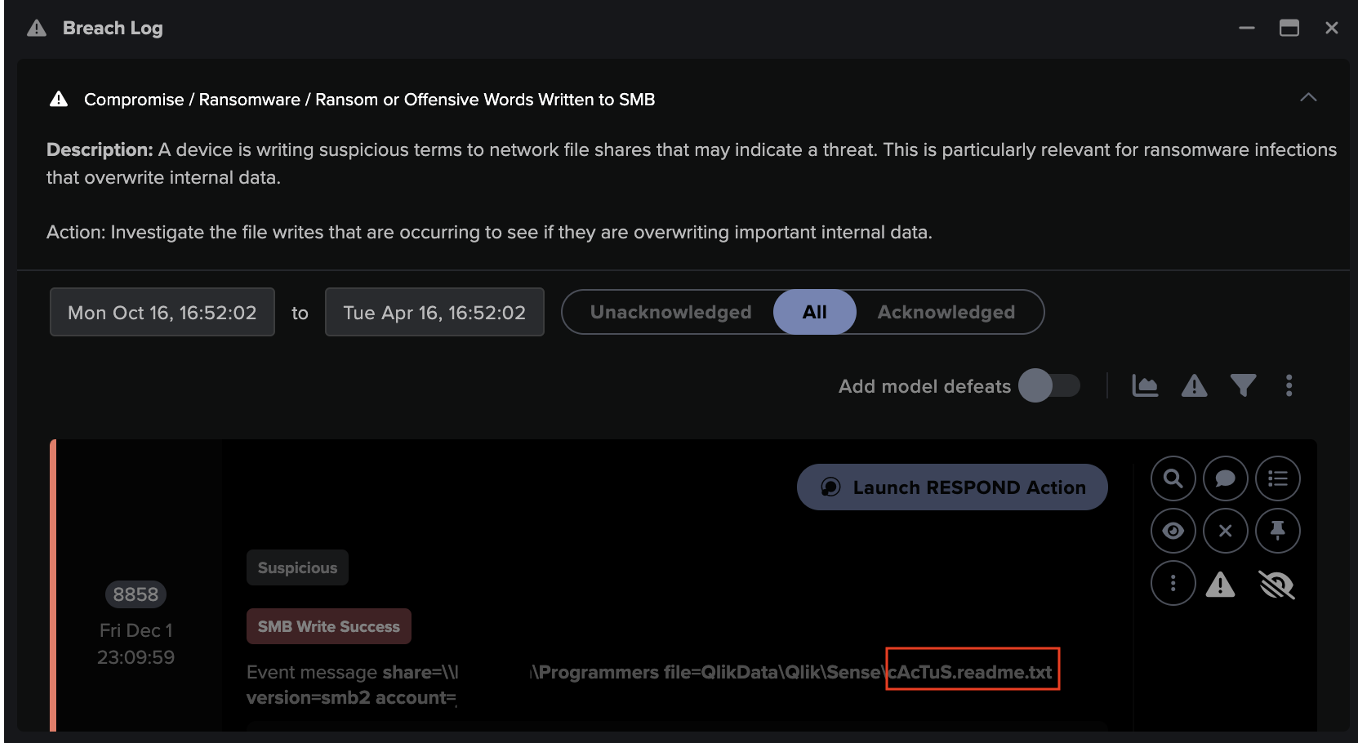
![Cyber AI Analyst Incident Log showing the offending device making over 1,000 connections to the suspicious hostname “zohoservice[.]net” over port 8383, within a specific period.](https://assets-global.website-files.com/626ff4d25aca2edf4325ff97/662971c1cf09890fd46729a1_Screenshot%202024-04-24%20at%201.55.10%20PM.png)